02
The correlation between climate change and the rise in diseases
Health authorities worldwide, including the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), have been warning of an increasing risk of pathogenic, communicable disease outbreaks in countries across the globe, worsened by the impact of climate change.
Several studies have shown direct links between climate change and zoonotic diseases and a recent study by researchers at the University of Hawaii indicates that over 200 infectious diseases have been exacerbated by climate change.
Climate hazards exacerbate diseases
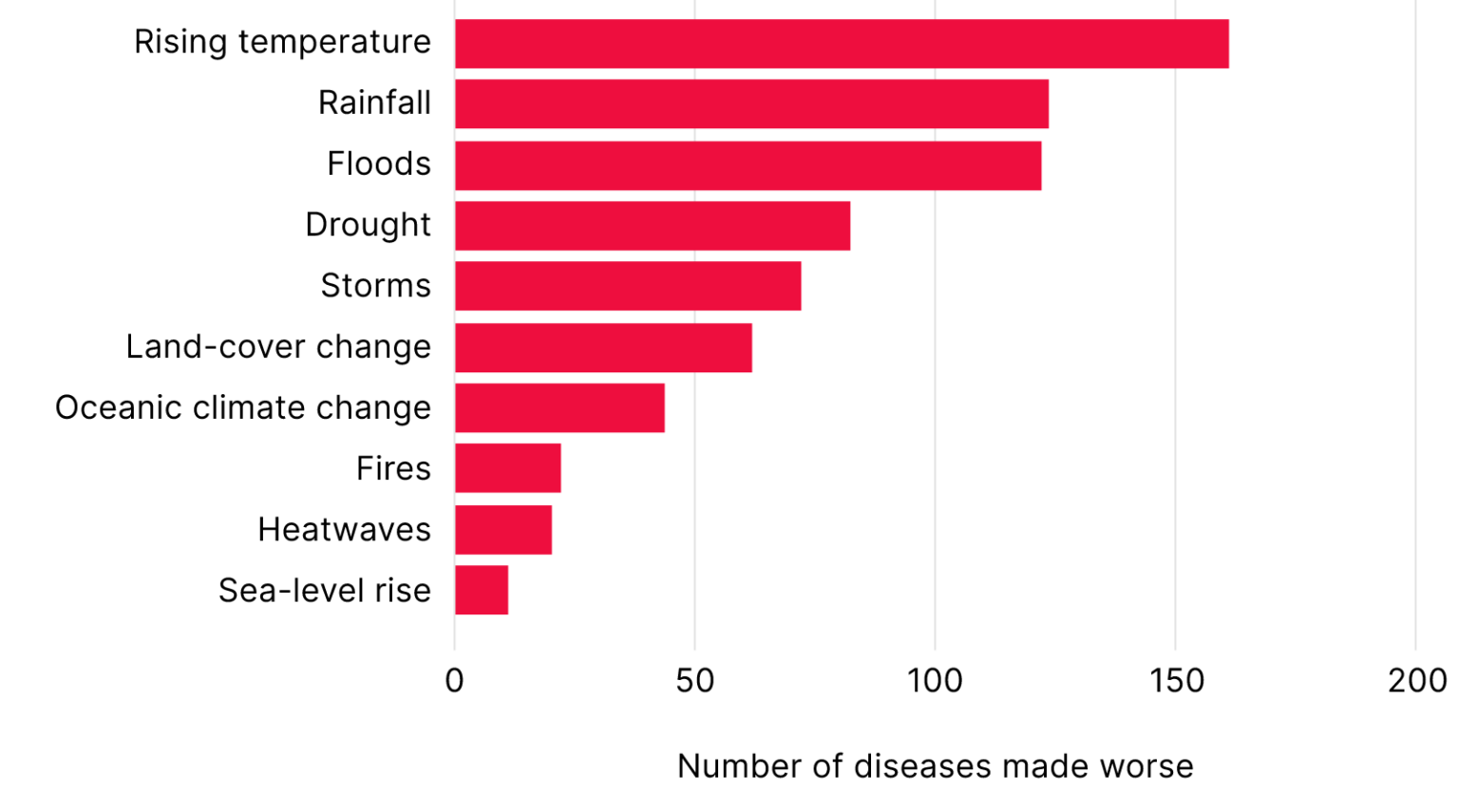
Source: Nature.com
Climate change often has swift and devastating effects on entire ecosystems, which disrupts the balance between different species and increases the risk of cross-species disease transmission, as witnessed during the COVID-19 outbreak.

Source: DownToEarth
In South and Southeast Asia, cases of mosquito-borne diseases, particularly dengue fever, have increased due to longer and more severe rainy seasons. Between June and October 2022, for example, Pakistan witnessed the worst flooding in a decade, and officials reported outbreaks of water-borne and vector-borne diseases in the flooded areas, particularly acute diarrhoea, dengue fever, malaria and typhoid fever.
In the United States (US), mild winters and rising temperatures have led illnesses caused by mosquito, tick and flea bites to more than double between 2004 and 2018. Climate change is also influencing the spread of Ebola in Central Africa.
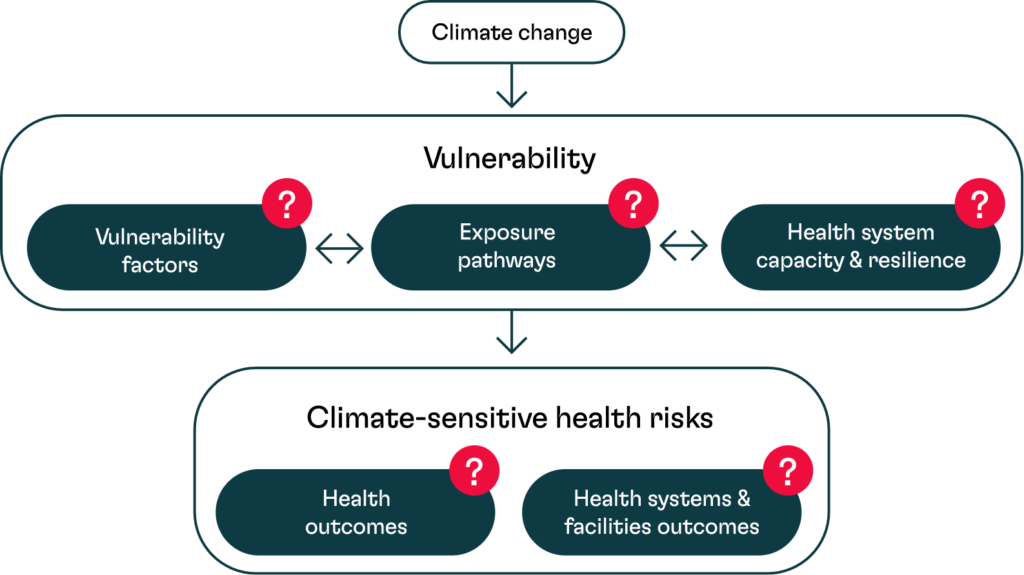
Demographic factors
Geographic factors
Biological factors & health status
Sociopolitical conditions
Socioeconomic factors
Extreme weather events
Heat stress
Air quality
Water quality & quantity
Food security & safety
Vector distribution & ecology
Leadership & governance
Health workforce
Health information systems
Essential medical products & technologies
Service delivery
Financing
Injury & mortality from extreme weather effects
Heat-related illness
Respiratory illness
Water-borne diseases & other water-related health impacts+
Zoonoses
Vector-bourne diseases
Malnutrition and food-bourne diseases
Noncommunicable diseases (NCDs)
Mental & psychosocial health
Impacts on healthcare facilities
Effects on health systems
Source: WHO
Although scientific data on the spillover of the virus from animal hosts to humans is limited, studies have projected that the rate will increase manifold in the coming years as temperatures rise and rainfall becomes more irregular.
It is thus abundantly clear that even in a post-COVID-19 world, other kinds of health crises remain a threat.
By Avantika Deb

